Home > Sections > The Universe > Neptune
Last Updated: 14th June 2023
ARCHIVED ITEM: this page is no longer updated.
Neptune
Keywords
Neptune, ice planet, wind storms, Le Verrier, Oceanus, hydrogen, helium, methane, ammonia, rock core, Scooter, Triton, Despina.
Introduction
Not visible to the naked eye, Neptune was discovered using mathematics instead of being discovered through use of telescopes. It is situated more than 30 times as far from the Sun than the Earth.
Planet Features
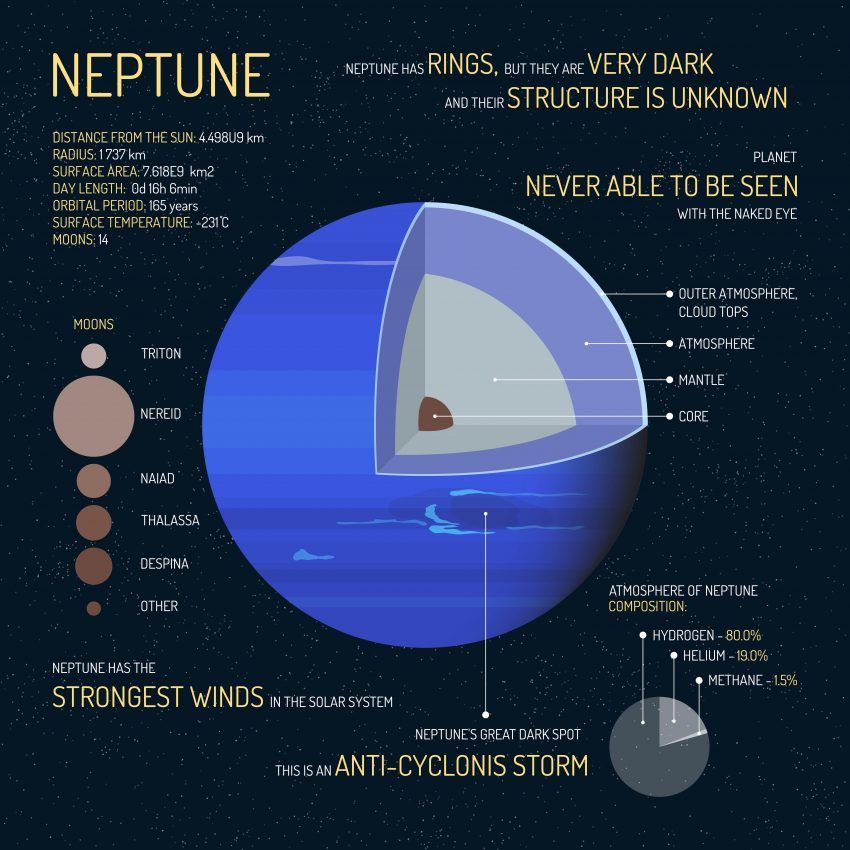
Size: four times the size of Earth, Neptune is on par with Uranus in size.
Visual Appearance: Neptune is a mass of hot, dense fluid of "icy" materials - a mixture of ammonia, water and methane. You can visibly see the wind storms on the planet (through a telescope).
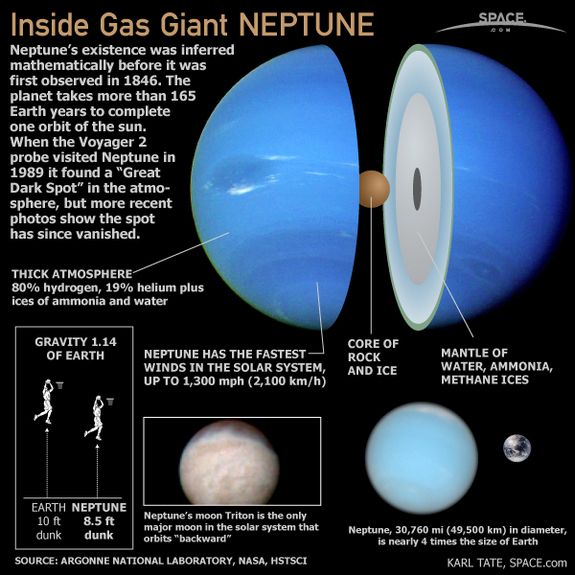
Structure: a rock core with an icy mantle and gaseous atmosphere, Neptune is home to some of the strongest winds. The gaseous atmosphere is mostly comprised of Hydrogen, Helium and Methane. There is no land on Neptune. The atmosphere gradually becomes liquid, and then an icy core.
Name: Neptune is named after the Roman god of the sea, an apt name as Neptune is as blue as the oceans. Other names were mentioned, including Oceanus, and even Le Verrier, the original mathemetician who discovered the planet through calculations.
Interesting fact: Pluto and Neptune's orbits cross over, but they never collide.
More: Neptune has 14 known moons, and one of which is called Despina who was Neptune's daughter. Another moon, Triton, has some of the lowest temperatures in the Solar System, with temperatures as low as -235° Celcius (-391° Farhenheit). It even has volcanoes that erupt ice.
A wisp of something that is white is nicknamed "Scooter" that travels around Neptune at different intervals. Scientists still wonder what it is. Methane is the reason the colour of Neptune is blue. Methane absorbs red light and reflects blue colours.
Here is a YouTube video from National Geographic on Neptune:




 Earth
Earth