Home > Sections > The Universe > Earth
Last Updated: 14th June 2023
ARCHIVED ITEM: this page is no longer updated.
Earth
Keywords
Earth, moon, seasons, atmosphere, rotation, axis, tidal lock, most dense, water, gravity, tectonic plates.
Introduction
Earth is our home. We know it for many different reasons - giving us life, providing us with somewhere in the world to stay, and also for te many, many species of other organisms in the planet. It is the only habitable planet that we know of, and is around 4.5 billion years old.
Planet Features
Size: being slightly bigger than the four planets closest to the Sun, Earth is often comparable with Venus and Mars. It is roughly 7,918 miles (12,742 kilometres) in diameter, and one astronomical unit from the Sun. This makes it easier to measure objects in space in distance from the Sun.
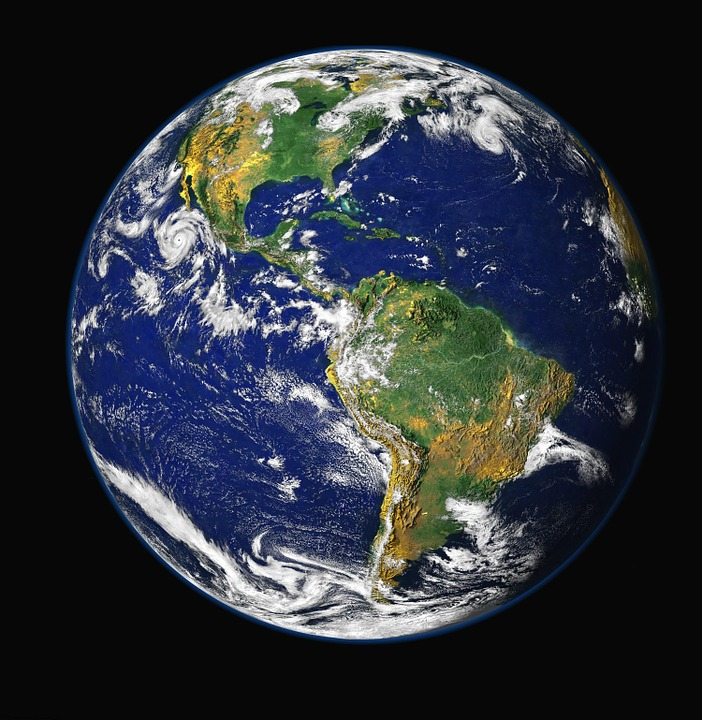
Visual Appearance: consisting of 70% water, from space, Earth looks like a blue planet. Land masses are spread around the planet in a fashion, and they form in seven continents. You can see clouds from space, and also differences in terrain (temperate is green, desert is brown, and oceans are blue).
If you look up at the Moon from Earth, it can appear white, grey, yellow, blue and red, depending on the time of year, and what is happening (due to the position of the Sun).
Interesting fact: the Earth is not, in fact, round. By 0.3%. Which is very much minimal. But, at the equator is is that much thicker than the rest. It still looks circular and round from space though.
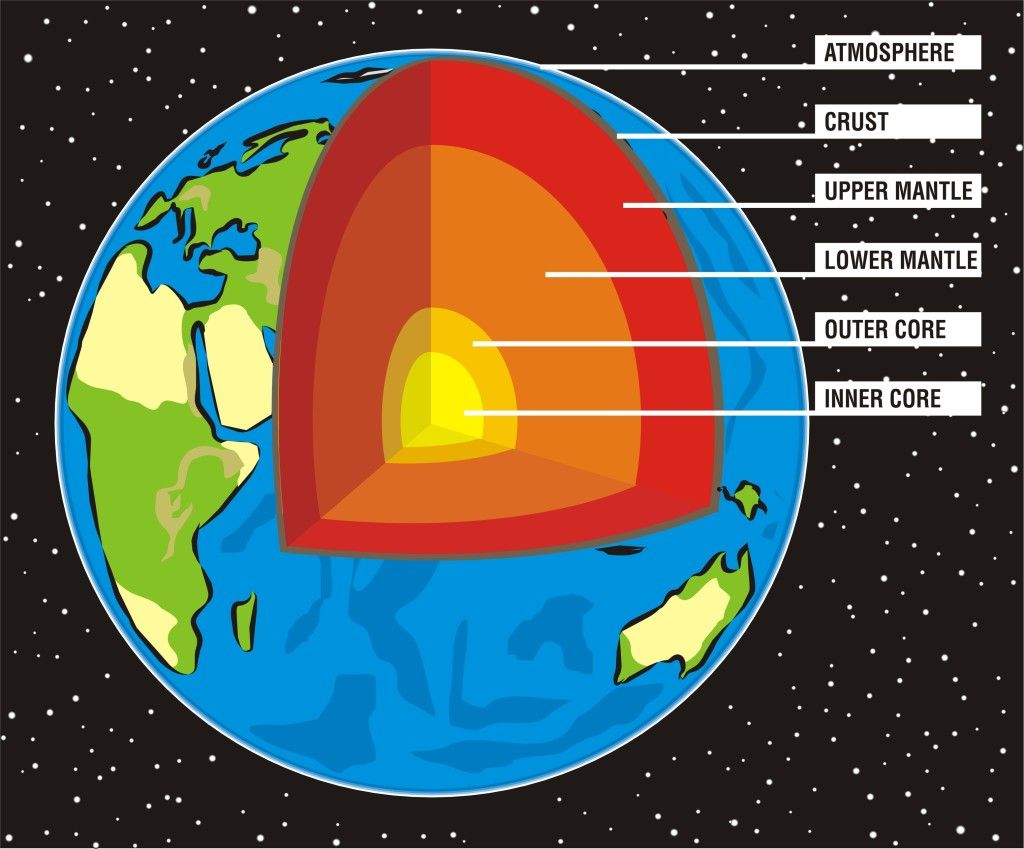
Structure: made from an inner core of molten iron and nickel, the Earth has four different layers - the core, the lower mantle, the upper mantle and the crust. It's structure enables the crust to terraform - tectonic plates move around the world at a slow rate and either go back underneath into the crust, or are pushed upwards to make mountains. They also move apart (Iceland is always expanding as a result), and form a new layer of land.
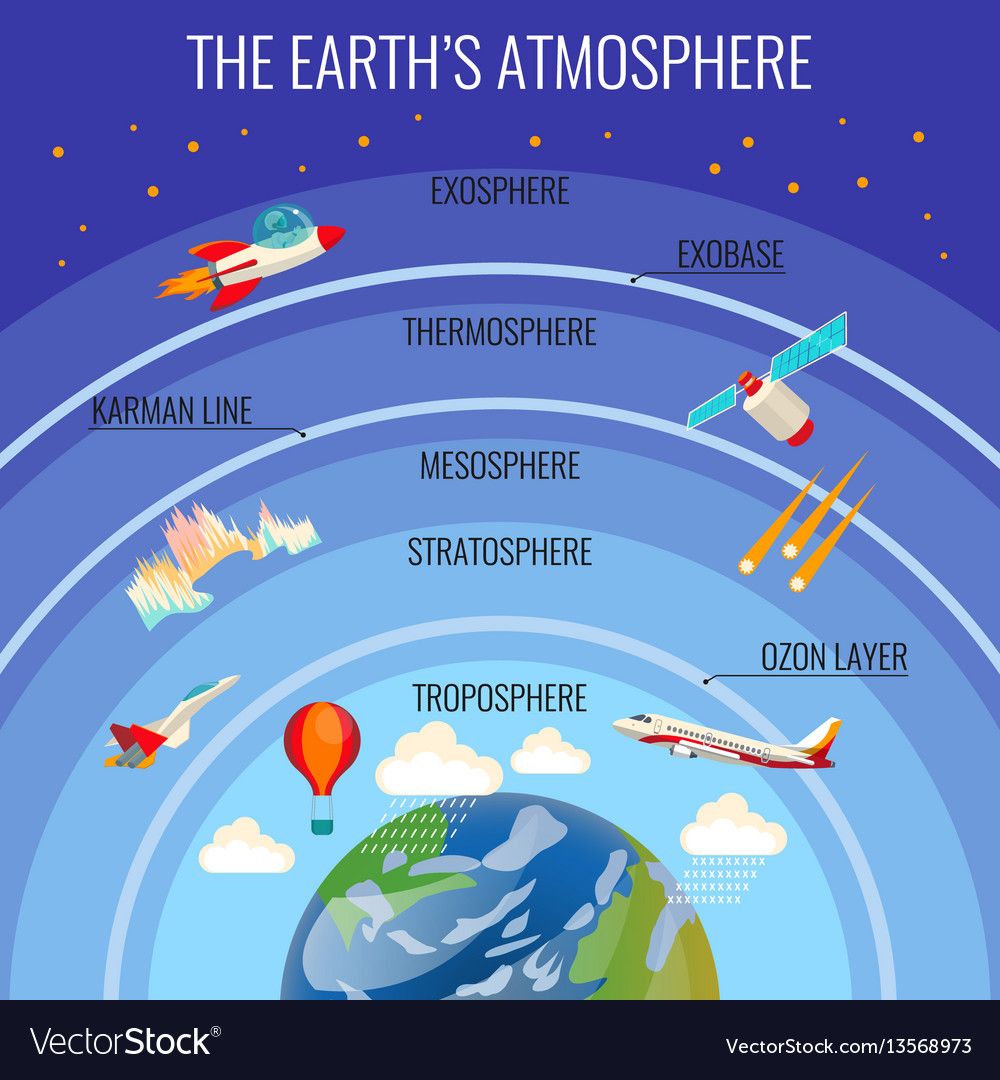
The atmosphere on our planet is split into 5 layers. Each layer allows for a certain amount of radiation from the Sun to pass through (in the form of Ultra Violet (UV) rays). The troposphere is the closest to the Earth, and here is where we see clouds, and aircraft flying across the sky. The rest allows for us to see things like meteors, both auroras (Borealis and Australis), satellites that orbit the Earth and space craft, such as the International Space Station.
Name: the name Earth has only been around for around 1,000 years. Although all the of the other planets are named after Greek or Roman gods or goddesses, Earth is a Germanic word meaning "the ground". This is also translated across different languages as the same.
More: we have an atmosphere like no other in the known universe, enabling all manner of lifeforms to survive and thrive. It enabled life some 4.5 billion years ago in the form of single-celled bacteria, and has had five extinction level threats during this period where organisms have had to evolve.
Earth is tidally locked with the Moon, which is our only celestial satellite. This means that we only see the one face of the Moon, as it rotates around us facing the same way.
Here is a YouTube video from National Geographic about Earth:
Forget Space Exploration
Instead of exploring space (which by the way, is fine), we should really be exploring this planet still. There are still uncharted waters, which are deeper than any man or woman can currently go. Even robotic devices struggle to go as deep as the deepest oceans, due to the presure that the water creates.
We still have millions of species of organisms to discover on this planet as well. So, while we while away the time exploring parts of space, we could also be doing the same in our own planet to find out more about it.




 Venus
Venus Ecosystems
Ecosystems