Home > Sections > The Universe > The Moon
Last Updated: 14th June 2023
ARCHIVED ITEM: this page is no longer updated.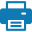
The Moon
Keywords
Moon, satellite, orbit, tidal lock, dark side of the Moon, gravity, astronauts, Neil Armstrong, Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin, Michael Collins.
Introduction
The Moon is the closest celestial body to us, as it rotates around the Earth. It is the only other place humans have stepped foot, and is situated around 239,000 miles (385,000 kilometres) from our planet.
Features of the Moon
Size: the Moon is smaller than the Earth by some degree, and if we were to put it into perspective, if you get a pound coin, and place a pea next to it, that's the relative sized of the Earth (coin) and the Moon (pea).
Visual Appearance: in space, it is grey in colour, with impact marks from various impacts of other space materials that have hit it over the billions of years it has been present. Original thoughts of the Moon were that it had hit our planet at some point during the creation process, and this is partly true, as when the Sun formed, there were two close objects (Earth, and Theia - another protoplanet) that crashed into one another. When they solidified, they formed both the Earth and Moon.
Interesting fact: one person has played golf on the Moon. Alan Shepard, a member of NASA and who walked on the Moon in 1971. When he did, he decided to play with the Moon's gravity and took two shots with a homemade golf club. The balls were never retrieved.
Structure: similar to the way Earth is structured, the moon also have a dual core. Part of it is liquid, and the other part is solid. It also has a partial melt - an area of the mantle is part liquid, and when the melting points of both the solid and liquid forms are different. Outside the melt is the upper mantle, and then the crust, which is then split between lunar maria (seas on the moon) and lunar terrae, which are the major geological provinces on the Moon.
Name: we gave the Moon it's name before we found more moons, so it is simply called the Moon. Galileo discovered four moons around Jupiter in the 1600s, which were given their respective names, but the Moon kept it's name.
More: the Moon is in a tidal lock with the Earth. This means that it is constantly in the same position and doesn't rotate on it's own axis while orbiting the Earth. This helps to sustain the wobble of our own planet's axis, as well as climate control, and the tides in the seas and oceans.
The Moon has a gravity of it's own, though it's not as strong as Earth's, being 0.6 that of our planet. This means you feel more weightless on the Moon, and objects can fly or move further than in our gravity. This is why when you see videos of the astronauts walking or running, they look like they are bobbling along with ease.
During the early 1960s, a space race began. During 1961, then president John F. Kennedy vowed that there will be men on the Moon before the end of the decade, and sure enough, even with him being shot in 1963 and pressures from government, the Apollo 11 mission in 1969 sent three young astronauts to the Moon where they walked and collected data and moonrocks. Neil Armstrong, Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin and Michael Collins all went to the Moon in the Lunar module. It was a feat that no one else had achieved before, despite competition from the then Soviet Union (now Russia). Michael Collins didn't actually walk on the Moon, he was in the Lunar module the whole trip and piloted the craft to safety there and back. There have only been twelve people land and walk on the Moon, the last being Harrison Schmitt in December 1972. There are plans for people to go back to the Moon, but this is in it's infancy, as there are plans to put people on Mars as well.
Also, because we only see the one side of the Moon, when it's in the sky at various points during the year, it changes shape. Not literally, but due to the position of the Sun during the evenings, the Moon looks like it becomes a crescent and other various circular shapes. We call these phases. Long has it been tradition that a full Moon (when we see the whole face of the Moon) is when a wolf will howl and turn into a werewolf. But these are just fairy tales.
Because of the position of the Sun, the Moon can change colour. This is purely to do with interaction from both the Sun and our atmosphere. A red or yellow moon can be because it is low to the horizon, a blue moon (rarer to see) is due to there being more dust particles in the atmosphere, and even during a total eclipse of the Moon, it can appear a very dark red, which is due to light refracted through the air around the Earth.
Here is a YouTube video from National Geographic about the Moon:
Footnotes
[1]Phases of the Moon, image provided by  Freepik.
Freepik.




 Earth
Earth Moon Phases
Moon Phases