Home > Sections > Energy > Energy Resources
Last Updated: 14th June 2023
ARCHIVED ITEM: this page is no longer updated.
Energy Resources
Keywords
Energy, resource, renewable, non-renewable, coal, oil, gas, fossil fuel, hydroelectric, wind, solar, crude oil, geothermal, tidal, hydrothermal, nuclear.
Introduction
We all use energy. But we all use it in form of electricity. How is it made, and what resources do we use to make it?
Types of Resource
There are many types of energy resources. They provide us with the electricity we need, as well as do other things like heat our homes, provide us with a means of transport and give us the ability to do minor tasks like mow the lawn.
Non-Renewable Resources
We all know what fossil fuels are - coal, oil and gas. We still use these, and have been since the Industrial Revolution in the 1800s.
They provide us with the use of petrol and diesel for cars, aircraft fuel (kerosene), bitumen for roads, lubrication products like oil and waxes, fuel for central heating, and other chemicals we use in processing plants and manufacturing.
They are considered a finite resource, and will eventually run out (the latest prediction is at around 2100), so companies are finding other ways to make products - just look at the way coffee cups are made now, some of them are made from entire recycled materials.
Renewable Resources
There are many types of renewable resources for energy. We use all of them to some extent, but we do not rely solely on them for power.
They include:
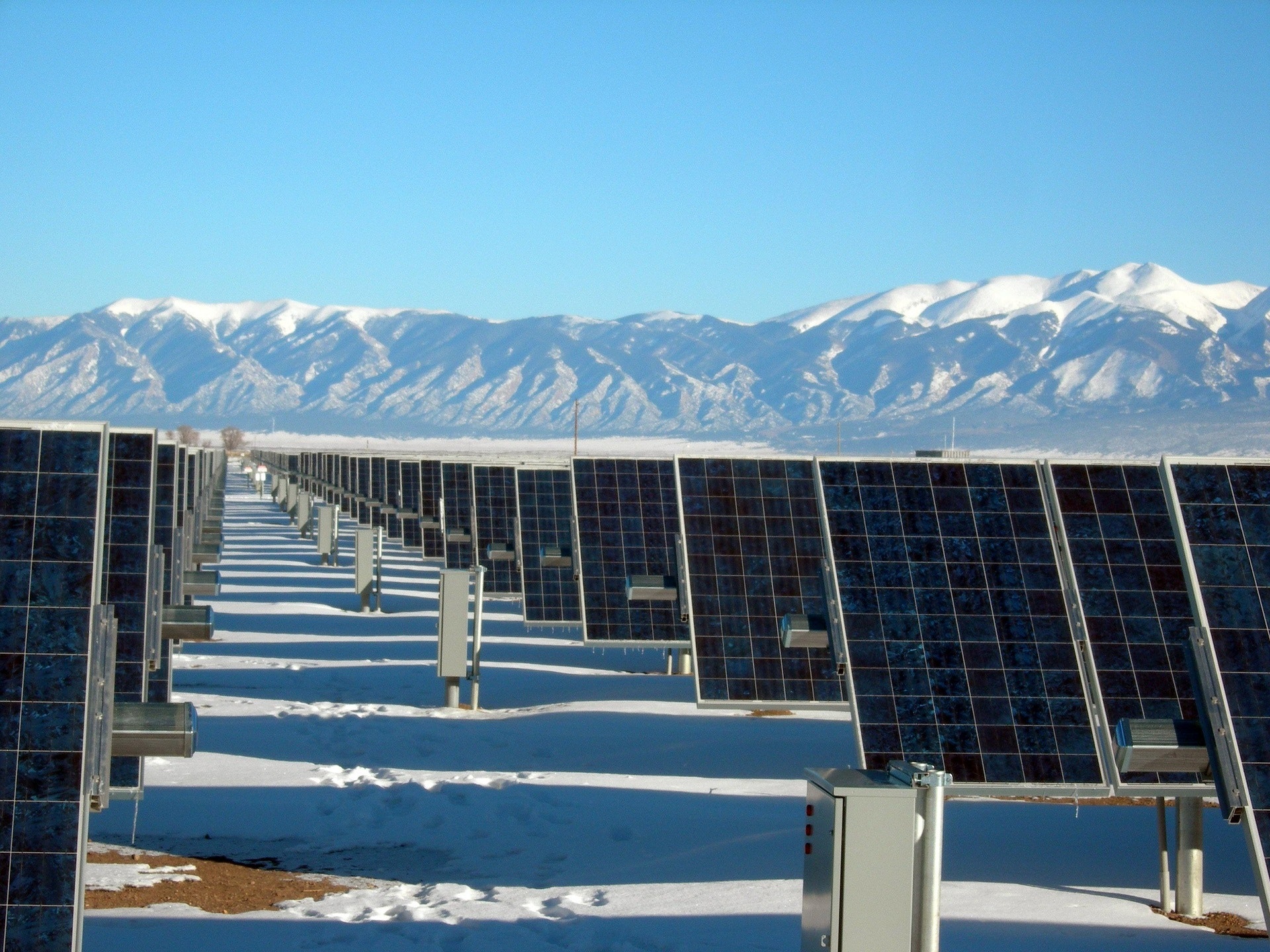
Solar: you would think that utilising the sun's energy would be easy, but in some countries, it can be difficult to use it due to the sun being under clouds a lot of the time. But using solar panels to generate electricity is a renewable source, as the sun is always there to provide energy.
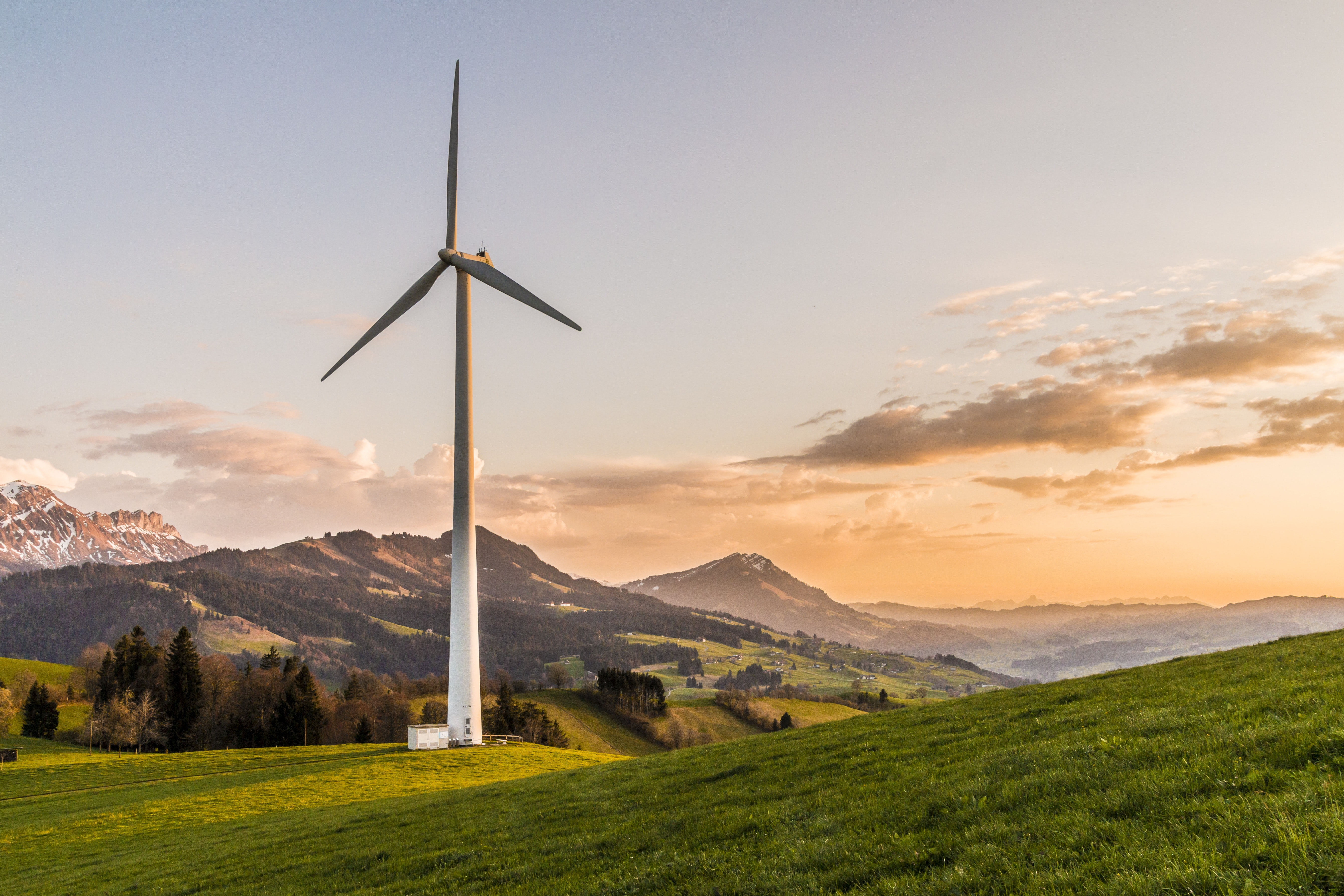
Wind: no, not that type of wind; just the wind that is in the environment. Great big wind turbines turn when the wind blows, and generates electricity. One turbine can provide enough energy for around 5 houses. If you look out on the East coast, you will see (especially if you visit Clacton-on-Sea) large wind farms out to sea. Why? Because the wind is stronger out to sea, as there is nothing to stop it moving.
Hydroelectric: this is harnessing the power of water movement through pressures tubes that allow the generation of electricity. For example, a dam across a river or in a reservoir (like the Ffestiniog Power Station) can produce a lot of power in a small space of time if needed.
Interesting fact: hydroelectricity is the most widely-used renewable power source. It accounts for more than 54% of the global renewable power generated, and 18% of the world's total power generation.
Tidal: another way to harness the use of water is to use the power of the tides. Large funnel shaped turbines sit in the water, and are moved in a circular fashion to create energy.
Biomass: burning raw organic waste material creates energy. Once burned, it can be converted into clean products like steam, biodiesel and biofuels. This is a carbon neutral way of making energy.
Geothermal: created within the Earth, geothermal is a renewable source of energy, as it is constantly created.
Hydrothermal energy is created using liquid from underground, magma heats nearby rocks and underground aquifers, which is then released through geysers, hot springs and steam vents.
Dry geothermal can be accessed by drilling down, being enhanced with injected water to create steam.
Nuclear: this is using radioactive elements such as Uranium and Plutonium to create power. The most notable power stations known are Chernobyl (check out the disaster that happened in 1986), and Fukushima (again, check out articles from 2008 on this).
Take a look at this YouTube video from National Geographic about energy:
Advantages & Disadvantages
A lot of these resources are great. They provide us with energy needed to continue working, heating our homes or giving us transport options. But they each have their advantages and disadvantages.
For example, fossil fuels are finite. This means they will run out at some point. This also means we will have to find another way to run a car (enter the electric car), or heat our home (heat pumps).
Another disadvantage of fossil fuels is that they create a lot of pollution, even though modern technologies have halved this since the Industrial Revolution. They create a lot of carbon emissions, which then increases global warming and the production of greenhouse gases.
One advantage of them though is that they are readily available, and also that they provide a lot of energy. Just look at crude oil - it can be fractionally distilled into many many products for use in many components.
Renewable resources are great because they can continually provide you with an energy source. But the disadvantage is that it isn't harnessed enough, and also that it doesn't actually create enough energy without making a lot of the items needed (wind turbines, dams).




 Crude Oil
Crude Oil The Sun
The Sun Global Warming
Global Warming Environmental Impacts of Mining
Environmental Impacts of Mining

