Home > Sections > Elements & the Periodic Table > Compounds
Last Updated: 14th June 2023
ARCHIVED ITEM: this page is no longer updated.
Compounds
Keywords
Compound, mixture, element, chemical bonding, fixed ratio, covalent, ionic, electrostatic.
Introduction
We know that elements are a single substance, made up of atoms of the same type. But taking it one step further, what is a compound?
A Closer Look
So, we know that an atom is the smallest unit of matter anything can be made of, and that elements are the single substance that cannot be broken down any further by methods we use to do so. So, what about compounds?
The technical terminology of a compound is:
A substance made up of two or more different chemical elements combined in a fixed ratio.
So, what does that actually mean? Well, chemical bonding is a process that happens naturally, depending on the reactivity of an element. For example, using metals such as magesium and iron and opening them up to elements like oxygen, we get a natural reaction. They become magnesium oxide and iron oxide, respectively.
How They are Formed
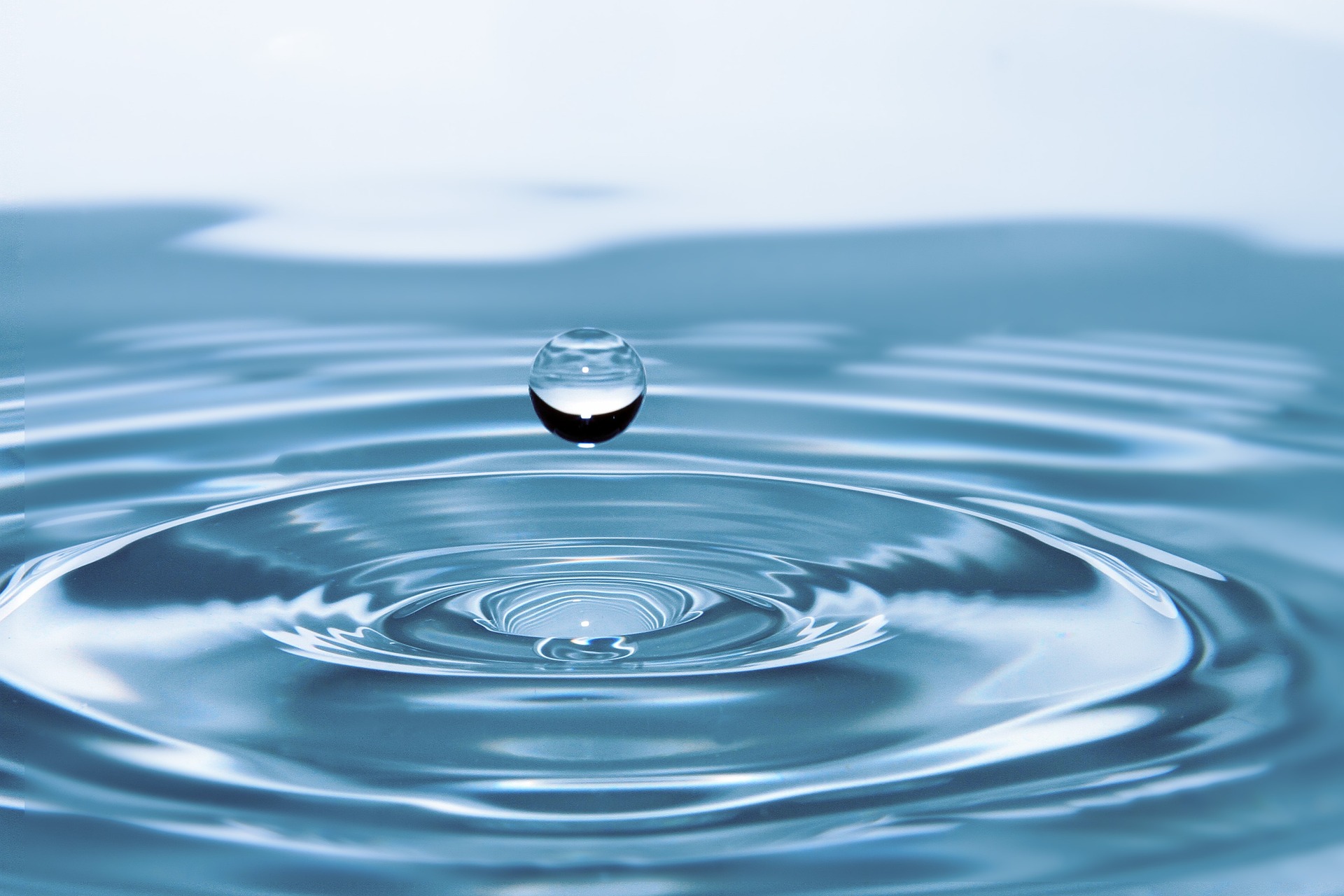
A compound is formed together through one of two ways - covalent or ionic bonding. Covalent bonding is where molecules are linked together to form a bond. An example of a covalent bond is water, or H2O. When they form together, they share electrons - one from hydrogen, and one from oxygen.
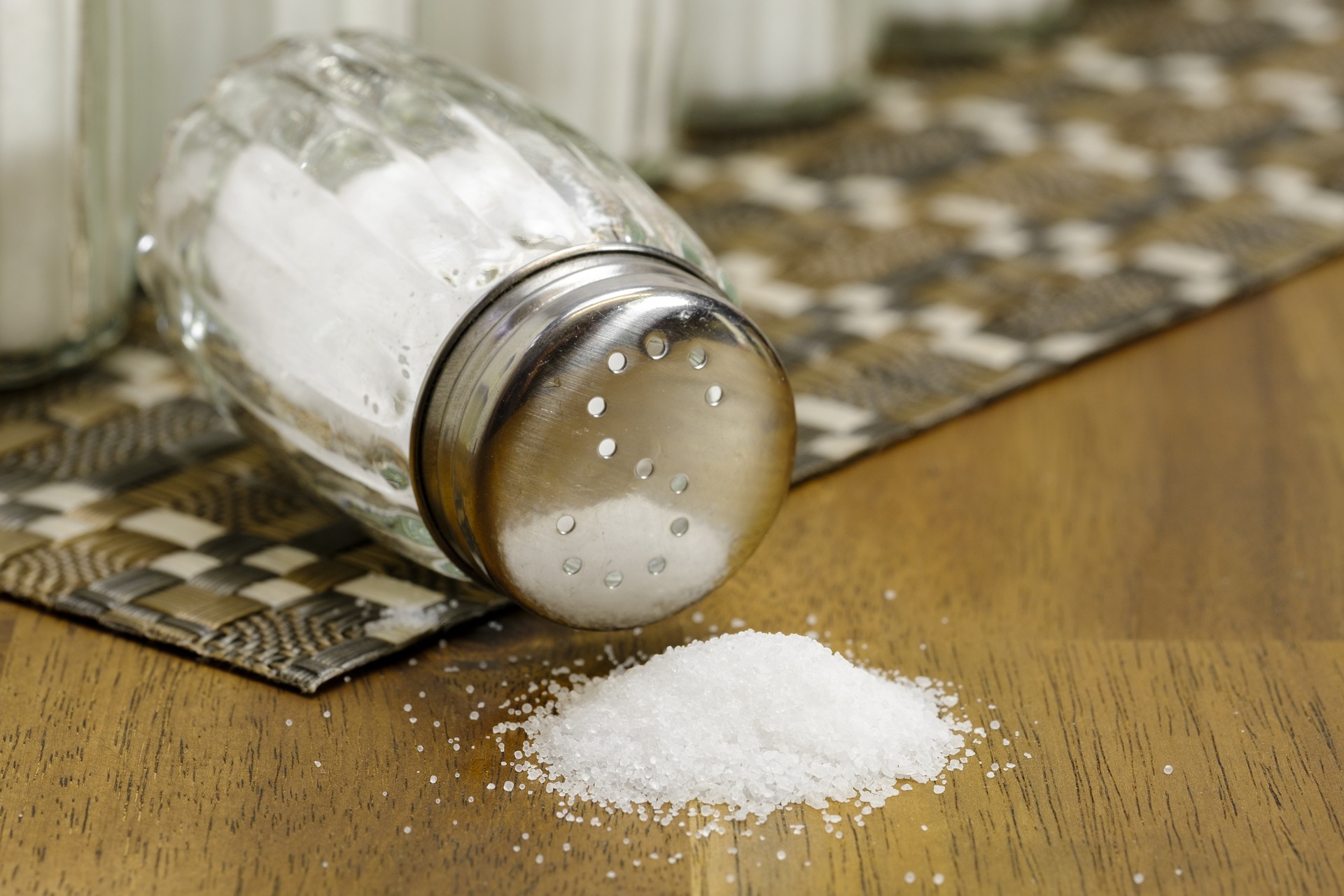
Ionic bonding is another form of chemical link that is caused by electrostatic forces between oppositely-charged ions in a compound. An example of this is salt. The elements sodium and chloride bond together ionically.
Interesting fact: a compound can be mixed with another compound to create a new compound. The chemical bonds when reacting together are broken and rebuilt as a new compound.
Here is a YouTube video from Fuse:
The Difference Between a Compound and Mixture
A lot of people confuse a compound with a mixture. There are two major differences.
In a mixture, while substances are combined, there's no chemical reaction or bonding. The individual substances in a mixture retain their own properties. They can also be separated into their individual elements.
A compound differs because there is a chemical reaction or bonding that occurs. When they do react, it can be difficult to separate them into their single component form. The amount of energy required to break them apart can be quite large.
Examples of compounds include:
- water (H2O)
- table salt (NaCl)
- baking soda




 Atoms
Atoms

