

Transpiration, translocation, evaporation, movement, liquid, phloem, xylem, stomata, cuticular, lenticular.
Plants and trees alike use a lot of water. An oak tree itself can soak up 50 gallons a day. But, what happens if there is too much water in it's systems?
Let's find out more.
If we look at the water cycle, we know that evaporation is the process where water changes it's state of matter to a vapour and rises up through the sun "drying" it out. This then turns into a cloud, and that cloud gets heavier and precipitates. It rains.
Now, excess water in plants and trees do a similar thing. They release excess water from their stomata, which in turn is soaked up by the sun in a similar process to evaporation. This is called transpiration.
The majority of the water retained in the plants are not used for growth or their metabolism, so while it is retained, it can be easily lost through transpiration.
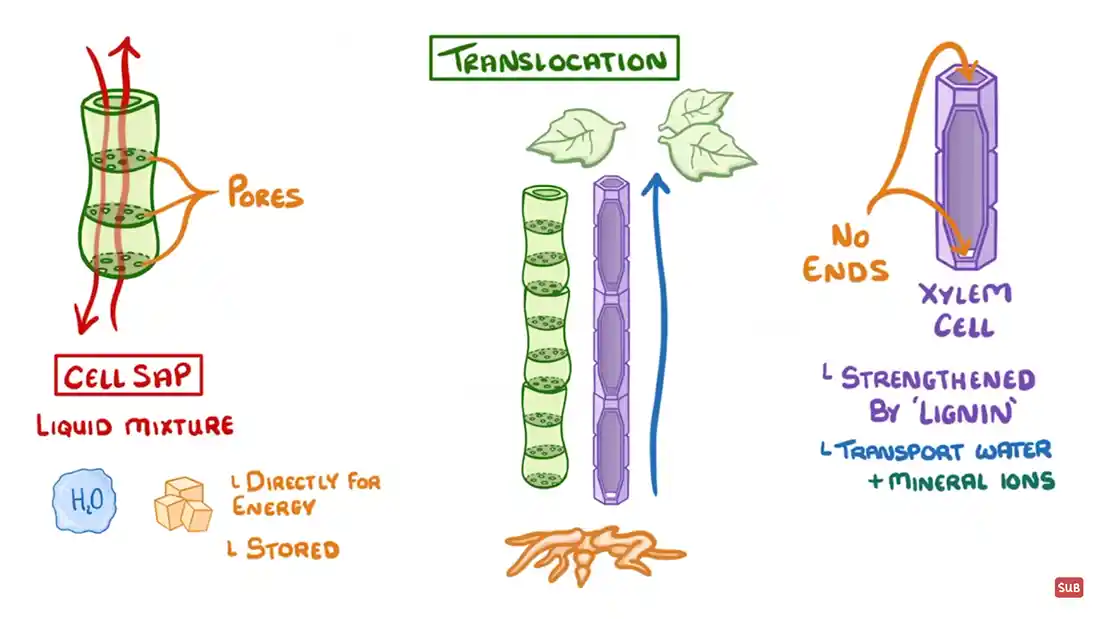
Inside the plant, a process called translocation happens. This is where the excess water is moved about the plant. It travels within the phloem, which is like a vein within the plant to allow movement of nutrients and sugars and other liquids.

Aphids suck the sap out of plants. This is done by sticking a tube into the plant's phloem and removing it from there. Ants farm the aphids as they are sweet, carrying the sap from the plants.
Phloem are cells, each with a semi-permeable membrane, that are bunched together to form tubes, and it's along these tubes that the water and sugars travel. Because phloem allow for transport both ways, it can travel in any direction around the plant. Depending on where the sugars are going, they can be dropped off at any point, or they can be stored within the plant somewhere until needed.
A xylem tube is a longer hollow tube that runs alongside the phloem, and is strengthened with lignin. It provides a direct access between the roots and the leaves for water and mineral ions that can then be used in photosynthesis.
There are different types of transpiration, depending on the location in the plant. They include:
The following still is from a video on transpiration and translocation, with the following details:
Please click on the image to view the video.
Disclaimer | About Me | Sitemap
Website design by SyntaxHTML.


Blue icons adapted from icons courtesy of Smashicons.com