Home > Sections > Energy > Speed
Last Updated: 14th June 2023
ARCHIVED ITEM: this page is no longer updated.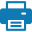
Speed
Keywords
Speed, fast, movement, motion, metres per second, kilometres per hour, miles per hour, distance, time.
Introduction
Let's face it, we all like to go fast. We can get to places quicker, or we can go round on a rollercoaster and go fast. Movement is depicted by speed. But, what is it?
Speed
Speed is a measure of how quickly something is travelling, or moving. It is measured in time units, usually metres per second, or kilometres per hour (km/h) and miles per hour (mph).
Speed = distance travelled / time taken
You can use the equation above to work out the speed you were travelling, by dividing the distance travelled by the time. It works any way round you wish to put it too, so if you wanted to find out how long it took, you divide the distance travelled by the speed.
Interesting fact: the fastest speed a human has travelled is during 1969 in the Apollo 10 mission. They reached a speed of 39,897km/h (24,790mph) during orbit around the Earth.
In context, it can look like this:
- Distance = Speed ÷ Time
- Speed = Distance ÷ Time
- Time = Distance ÷ Speed
Here is a YouTube video from Cognito about speed:
This can work for more than just cars. The obvious choice is to use vehicles, but you could also work out how fast you write by using the same equation. Figure it out by counting the amount of letters and numbers written, and the average length of them. Then you can figure out the average speed at which you write.
Distance-Time Graphs
A distance time graph can be used to determine how fast someone was moving at any given time. It determines the distance on the X axis, and the time unit along the Y axis. It then shows you how fast that person (or object) was moving over the period of time given.
It's a way to show the data in a presentation format. It uses the same principle as the triangle, using the equation of Speed = Distance over Time.
End Note
We have learnt that speed can be worked out by dividing the distance travelled by the time it took to do so. We have also learnt that it can be applied to many things in every day life.




 Weather Conditions & Braking Distance
Weather Conditions & Braking Distance