Home > Sections > Elements & the Periodic Table > Polymers
Last Updated: 14th June 2023
ARCHIVED ITEM: this page is no longer updated.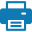
Polymers
Keywords
Polymer, monomer, polythene, polypropene, polystyrene, PVC, waterproof, chemical resistance, mouldable, propene.
Introduction
A polymer is the joining of many monomers to form a chain that make them waterproof, resistant to chemicals and can be moulded. But what does that all mean?
Let's take a closer look.
How are They Made?
If you take a chain-link fence, you start with one piece. That is a monomer. That single piece of link can be replicated to create more of the same. This is the same as a monomer. It can be recreated or duplicated as another one. When they are then linked together, they create a polymer. So, in the example of the chain-link fence, you would mould the first one, and then you would mould the second around the first, second and third, and so on.
Typically, polymers are made of a substance called propene. The chemical formula for propene is C3H6. Link these monomers of C3H6 together, and they become a string of C3H6 together. To make things simple, when writing these as a formula, you would normally write the main string (in this case, C3H6), and you would add a small n to the side of it, which represents the number. Each polymer has it's own number of chain links.
Properties of the Polymer
A polymer has many properties, including:
- it is waterproof
- resistant to chemicals
- it can be moulded
- it can be in liquid form (PVA)
- it can be in a solid form (Polystyrene)
Interesting fact: PVA glue is a liquid at room temperature, and is used as an adhesive, unlike most other polymers, which are solid at room temperature.
Melting and Boiling Points
Polymers react to different melting and boiling points, and what it does is breaks the bonds between each link in the chain by using intermolecular forces. They are weaker than their covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Because a polymer is so long, it has a high surface area.
Polymers have a much lower boiling point than other structures like a diamond, which have a giant covalent bond. However, they have a higher melting and boiling point than simple molecular substances - oxygen or chlorine. This is the reason why polymers are usually solid at room temperature.
Here is a YouTube video from Cognito on polymers: