

Kingdoms, animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, bacteria, eubacteria, archaeabacteria.
We began to classify all living organisms since we could write, and as a result, everything was classed as either an animal or plant. When we discovered there were many many more, we had to create new categories with which to classify them.
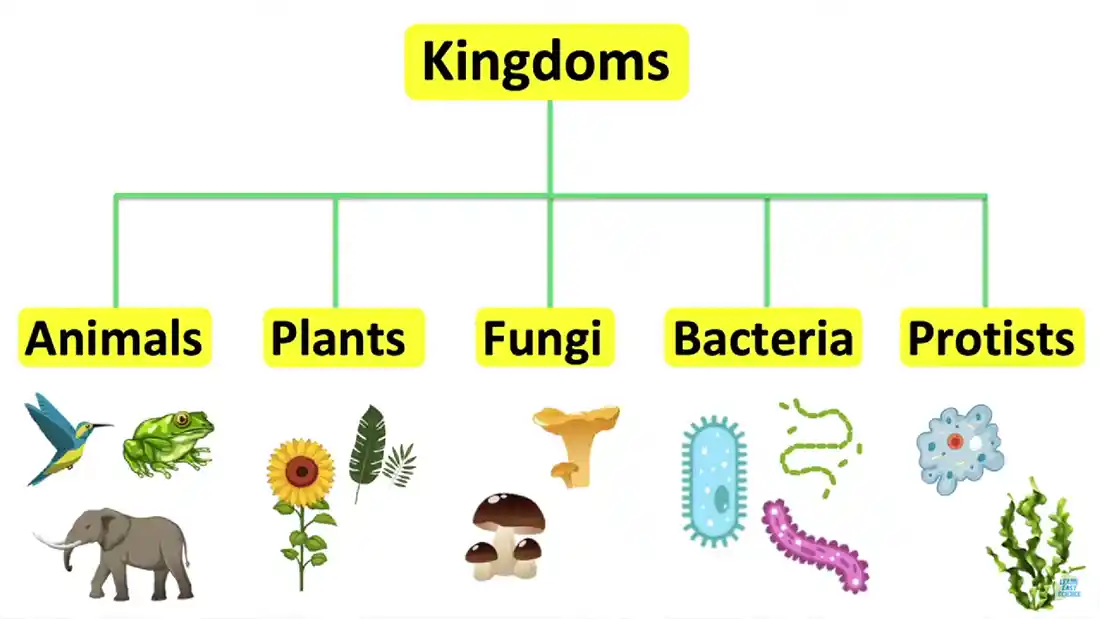
Here we look at the five (six) kingdoms created and what this means.
Probably the easiest to explain here, it is the kingdom that categorises the animals living on the planet. This means anything that we consider an animal - cat, elephant, hamster, fish, whale, polar bear, and so on - are classified within this kingdom.
So, as the name suggests, this is where all the plant organisms are categorised by kingdom. Every plant - Oak tree, chrysanthemum, daffodil, euphorbia, ferns - is placed here. Even aquatic plants go here.
From the mushrooms you can eat, to the deadly poisonous ones with the pretty colours, all fungi are categorised here. They also include single-cell fungi that are microscopic.

A series of rules is set out for each kingdom. While it may seem some organisms should be in one kingdom, they are placed into other kingdoms depending on different sets of criteria. They have to meet these criteria in order to be placed in the right one.
Any single-celled bacteria organism is placed into the bacteria kingdom. There are many, and some are also now known as Archaea.
There are both good and bad bacteria. This means that some bacteria (for example those that live within your digestive system) can help you with digestion of foods, or there are others (salmonella for example) that could potentially kill you if not treated correctly with medication.
What is a protist? Hmm, you could say that they are advanced bacteria cells. But they don't quite fit in with this theory. They are unicellular (single-celled), but they possess a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles (the bits inside that perform a job).
All lifeforms on the planet are distinguished as being either prokaryote or eukaryote. While bacteria and archaea sit within the prokaryote section, all other organisms are considered to be eukaryotes, including protists. So, while they have features like bacteria, they are in fact considered more like a plant or animal, just within their own category.
While bacteria and archaea are often put together for their similarities, a recent study has shown that actually, they should be considered to be split in two.
In this case, bacteria are redefined as Eubacteria, and archaea is redefined as archaebacteria. Specifically, archaebacteria are bacteria cells that fall within the archaebacteria kingdom.
The following still is from a video on kingdoms, with the following details:
Please click on the image to view the video.
Disclaimer | About Me | Sitemap
Website design by SyntaxHTML.


Blue icons adapted from icons courtesy of Smashicons.com