

MRSA, methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, hospital, infection, swelling, warmth, pain, pus, redness, prison, nursing home, antibacterial cream, antibacterial soap.
An antibiotic resistant infection, MRSA is most often found and contracted in hospitals. It can also be found outside of hospitals as well. As well as being resistant to antibiotics, it can also cause other infections to present themselves, such as pneumonia.
Often cited as being one of the first superbugs known to man, the reason it got this name is because half of the antibiotics that could treat the infection don't work. This is due to the infection itself being resistant to a broad-spectrum group of antibiotics called Beta-lactam.
Most common in hospitals, nursing homes, prisons and care homes, people who have low immune systems and invasive devices such as a catheter and open wounds are more susceptible.
If you contract MRSA, it is not at first noticeable, and lays on your skin. If it gets any deeper than your skin, the symptoms include:
MRSA can live on a person and affects around 1 in 30 people. Where it resides is usually in the armpits, nose, groin, or buttocks. This is what is known as colonisation - a carrier of MRSA.
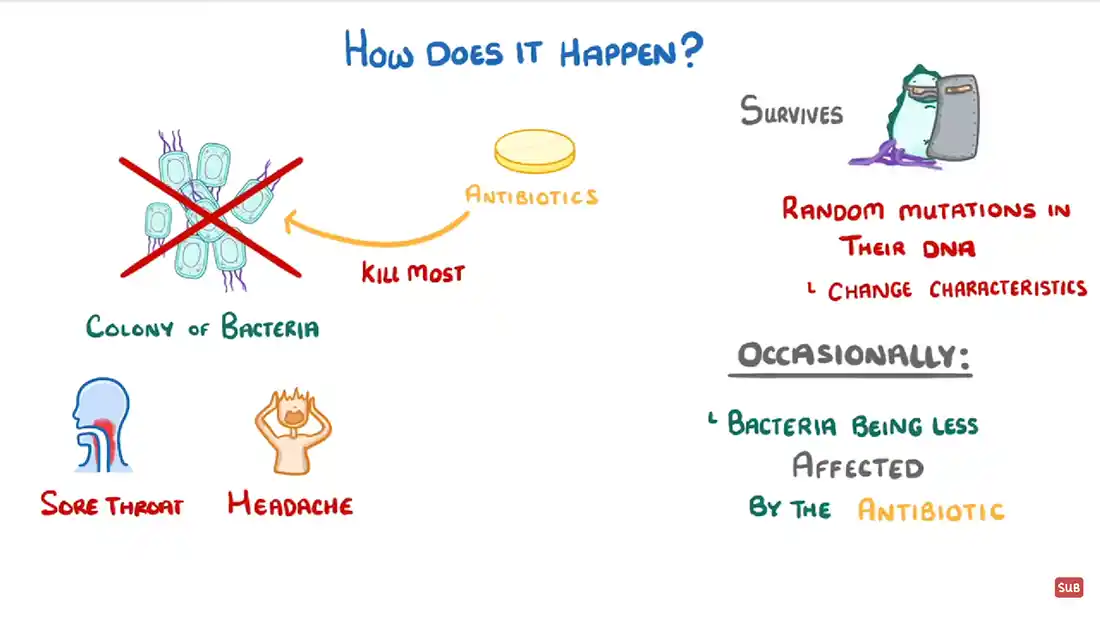
So, how do you get it?
You can get MRSA through the following:
If you get MRSA, you may not notice it at first, as it lays dormant on your skin. This could also make it go away naturally after a few hours, days or weeks, depending on your body's hygiene regime. If it goes deeper than your skin, it can cause irritation and become more serious.
The following still is from a video on MRSA, with the following details:
Please click on the image to view the video.
So, as mentioned before, you can get it when you stay in hospital for any length of time. People staying in hospital are at higher risk of getting it because:

MRSA also has a non-hospital variant, called Community associated MRSA (Ca-MRSA), which starts like impetigo and hurts.
There are several ways to detect MRSA. If you're going in for a stay at hospital, you will usually have a pre-admission check done by the nurse, who will swab you over your skin, and the results will return within a few days. Then, you will be notified as to whether you have it or not.
Treatments include one of the following:
Disclaimer | About Me | Sitemap
Website design by SyntaxHTML.


Blue icons adapted from icons courtesy of Smashicons.com